Gini Index
June 3, 2019
基尼系数
\[G = 1 - \sum_{i=1}^k p_i^2\]基尼系数和信息熵有着一样的性质
基尼系数越高,不确定性越强
在二分类问题中:$G = 1 - x^2 - (1 - x)^2 = -2x^2 + 2x$ 是一个开口向下的抛物线,在对称轴处取得最大值
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data[:,2:]
y = iris.target
def plot_decision_boundary(model, axis):
x0, x1 = np.meshgrid(
np.linspace(axis[0], axis[1], int((axis[1]-axis[0])*100)).reshape(-1, 1),
np.linspace(axis[2], axis[3], int((axis[3]-axis[2])*100)).reshape(-1, 1),
)
X_new = np.c_[x0.ravel(), x1.ravel()]
y_predict = model.predict(X_new)
zz = y_predict.reshape(x0.shape)
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
custom_cmap = ListedColormap(['#EF9A9A','#FFF59D','#90CAF9'])
plt.contourf(x0, x1, zz, cmap=custom_cmap)
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
dt_clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=2, criterion="gini", random_state=42)
dt_clf.fit(X, y)
DecisionTreeClassifier(class_weight=None, criterion=’gini’, max_depth=2, max_features=None, max_leaf_nodes=None, min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None, min_samples_leaf=1, min_samples_split=2, min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, presort=False, random_state=42, splitter=’best’)
plot_decision_boundary(dt_clf, axis=[0.5, 7.5, 0, 3])
plt.scatter(X[y==0, 0], X[y==0, 1])
plt.scatter(X[y==1, 0], X[y==1, 1])
plt.scatter(X[y==2, 0], X[y==2, 1])
plt.show()
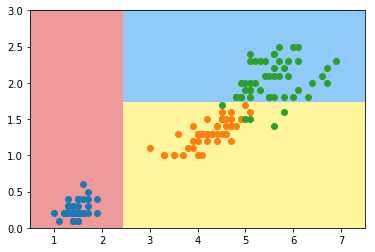
模拟尼基系数划分
from collections import Counter
from math import log
def split(X, y, d, value):
index_a = (X[:,d] <= value)
index_b = (X[:,d] > value)
return X[index_a], X[index_b], y[index_a], y[index_b]
def gini(y):
counter = Counter(y)
res = 1.0
for num in counter.values():
p = num / len(y)
res -= p ** 2
return res
def try_split(X, y):
best_g = float('inf')
best_d, best_v = -1, -1
for d in range(X.shape[1]):
sorted_index = np.argsort(X[:,d])
for i in range(1, len(X)):
if X[sorted_index[i], d] != X[sorted_index[i - 1], d]:
v = (X[sorted_index[i], d] + X[sorted_index[i - 1], d]) / 2
X_l, X_r, y_l, y_r = split(X, y, d, v)
p_l, p_r = len(X_l) / len(X), len(X_r) / len(X)
g = p_l * gini(y_l) + p_r * gini(y_r)
if g < best_g:
best_g ,best_d, best_v = g, d, v
return best_g, best_d, best_v
best_g, best_d, best_v = try_split(X, y)
print("best_g =", best_g)
print("best_d =", best_d)
print("best_v =", best_v)
best_g = 0.3333333333333333
best_d = 0
best_v = 2.45
X1_l, X1_r, y1_l, y1_r = split(X, y, best_d, best_v)
gini(y1_l)
0.0
gini(y1_r)
0.5
best_g2, best_d2, best_v2 = try_split(X1_r, y1_r)
print("best_g =", best_g2)
print("best_d =", best_d2)
print("best_v =", best_v2)
best_g = 0.1103059581320451 best_d = 1 best_v = 1.75
X2_l, X2_r, y2_l, y2_r = split(X1_r, y1_r, best_d2, best_v2)
gini(y2_l)
0.1680384087791495
gini(y2_r)
0.04253308128544431