Logistic Regression Implement And Decision Boundary
April 30, 2019
实现逻辑回归
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
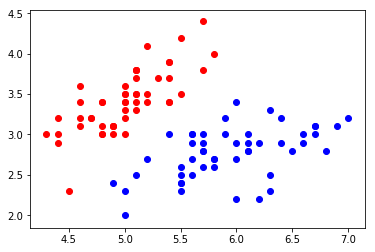
X = X[y<2,:2]
y = y[y<2]
X.shape
(100, 2)
y.shape
(100,)
plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1], color="red")
plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1], color="blue")
plt.show()
使用逻辑回归
LogisticRegression.py
import numpy as np
def accuracy_score(y_true, y_predict):
assert y_true.shape == y_predict.shape,\
"the size of y_true must be equal to the size of y_predict"
return (sum(y_true == y_predict) / len(y_true))
class LogisticRegression:
def __init__(self):
"""初始化Logistic Regression模型"""
self.coef_ = None
self.intercept_ = None
self._theta = None
def _sigmoid(self, t):
return 1. / (1. + np.exp(-t))
def fit(self, X_train, y_train, eta=0.01, n_iters=1e4):
"""根据训练数据集X_train, y_train, 使用梯度下降法训练Logistic Regression模型"""
assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0], \
"the size of X_train must be equal to the size of y_train"
def J(theta, X_b, y):
y_hat = self._sigmoid(X_b.dot(theta))
try:
return - np.sum(y*np.log(y_hat) + (1-y)*np.log(1-y_hat)) / len(y)
except:
return float('inf')
def dJ(theta, X_b, y):
return X_b.T.dot(self._sigmoid(X_b.dot(theta)) - y) / len(y)
def gradient_descent(X_b, y, initial_theta, eta, n_iters=1e4, epsilon=1e-8):
theta = initial_theta
cur_iter = 0
while cur_iter < n_iters:
gradient = dJ(theta, X_b, y)
last_theta = theta
theta = theta - eta * gradient
if (abs(J(theta, X_b, y) - J(last_theta, X_b, y)) < epsilon):
break
cur_iter += 1
return theta
X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X_train), 1)), X_train])
initial_theta = np.zeros(X_b.shape[1])
self._theta = gradient_descent(X_b, y_train, initial_theta, eta, n_iters)
self.intercept_ = self._theta[0]
self.coef_ = self._theta[1:]
return self
def predict_proba(self, X_predict):
"""给定待预测数据集X_predict,返回表示X_predict的结果概率向量"""
assert self.intercept_ is not None and self.coef_ is not None, \
"must fit before predict!"
assert X_predict.shape[1] == len(self.coef_), \
"the feature number of X_predict must be equal to X_train"
X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X_predict), 1)), X_predict])
return self._sigmoid(X_b.dot(self._theta))
def predict(self, X_predict):
"""给定待预测数据集X_predict,返回表示X_predict的结果向量"""
assert self.intercept_ is not None and self.coef_ is not None, \
"must fit before predict!"
assert X_predict.shape[1] == len(self.coef_), \
"the feature number of X_predict must be equal to X_train"
proba = self.predict_proba(X_predict)
return np.array(proba >= 0.5, dtype='int')
def score(self, X_test, y_test):
"""根据测试数据集 X_test 和 y_test 确定当前模型的准确度"""
y_predict = self.predict(X_test)
return accuracy_score(y_test, y_predict)
def __repr__(self):
return "LogisticRegression()"
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, seed=666)
log_reg = LogisticRegression()
log_reg.fit(X_train, y_train)
LogisticRegression()
log_reg.score(X_test, y_test)
1.0
log_reg.predict_proba(X_test)
array([0.92972035, 0.98664939, 0.14852024, 0.17601199, 0.0369836 , 0.0186637 , 0.04936918, 0.99669244, 0.97993941, 0.74524655, 0.04473194, 0.00339285, 0.26131273, 0.0369836 , 0.84192923, 0.79892262, 0.82890209, 0.32358166, 0.06535323, 0.20735334])
y_test
array([1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0])
log_reg.predict(X_test)
array([1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0])
log_reg.coef_
array([ 3.01796521, -5.04447145])
log_reg.intercept_
-0.6937719272911228
决策边界
\[\hat{p }= \sigma(\theta^T \cdot x_b) = \frac{1}{1 + e^{-\theta^T \cdot x_b}}\] \[\hat{y} = \begin{cases} 1,\quad \hat{p} \geq 0.5 \quad \theta^T \cdot x_b \geq 0\\\\ 0,\quad \hat{p} < 0.5 \quad \theta^T \cdot x_b < 0 \end{cases}\]此时$\theta^T \cdot x_b = 0$为决策边界
如果X有两个特征,可以写作$\theta_0 + \theta_1x_1 + \theta_2x_2 = 0$
或者写作
\[x_2 = \frac{-\theta_0 - \theta_1x_1}{\theta_2}\]可以表达为一条实线
def x2(x1):
return (-log_reg.coef_[0] * x1 - log_reg.intercept_) / log_reg.coef_[1]
x1_plot = np.linspace(4, 8, 1000)
x2_plot = x2(x1_plot)
plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1], color="red")
plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1], color="blue")
plt.plot(x1_plot, x2_plot)
plt.show()
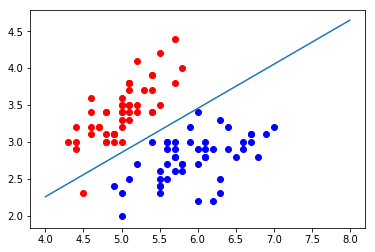
这根线就是我们说的决策边界
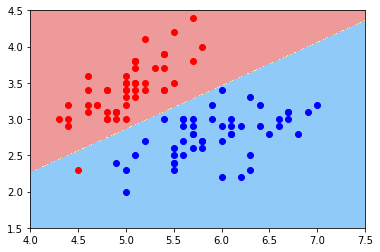
绘制不规则的决策边界
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
def plot_decision_boundary(model, axis):
x0, x1 = np.meshgrid(
np.linspace(axis[0], axis[1], int((axis[1] - axis[0]) * 100 )).reshape(-1, 1),
np.linspace(axis[2], axis[3], int((axis[3] - axis[2]) * 100 )).reshape(-1, 1)
)
X_new = np.c_[x0.ravel(), x1.ravel()]
y_predict = model.predict(X_new)
zz = y_predict.reshape(x0.shape)
custom_camp = ListedColormap(['#EF9A9A', '#FFF59F', '#90CAF9'])
plt.contourf(x0, x1, zz, cmap=custom_camp)
plot_decision_boundary(log_reg, axis=[4, 7.5, 1.5, 4.5])
plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1], color="red")
plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1], color="blue")
plt.show()
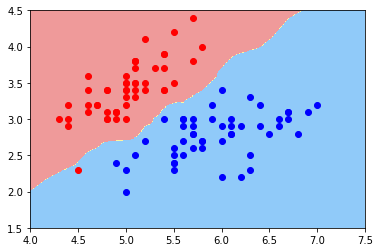
kNN 的决策边界
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
knn_clf = KNeighborsClassifier()
knn_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
KNeighborsClassifier(algorithm=’auto’, leaf_size=30, metric=’minkowski’, metric_params=None, n_jobs=1, n_neighbors=5, p=2, weights=’uniform’)
knn_clf.score(X_test, y_test)
1.0
plot_decision_boundary(knn_clf, axis=[4, 7.5, 1.5, 4.5])
plt.scatter(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1], color="red")
plt.scatter(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1], color="blue")
plt.show()
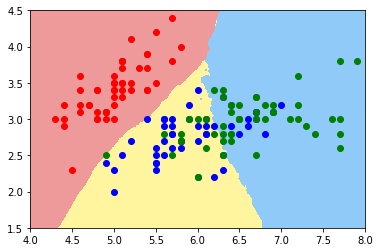
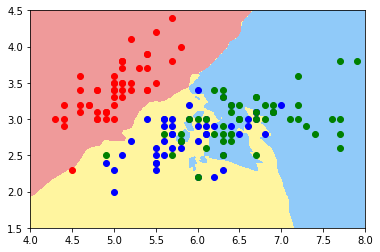
knn_clf_all = KNeighborsClassifier()
knn_clf_all.fit(iris.data[:,:2], iris.target)
KNeighborsClassifier(algorithm=’auto’, leaf_size=30, metric=’minkowski’, metric_params=None, n_jobs=1, n_neighbors=5, p=2, weights=’uniform’)
plot_decision_boundary(knn_clf_all, axis=[4, 8, 1.5, 4.5])
plt.scatter(iris.data[iris.target==0,0], iris.data[iris.target==0,1], color="red")
plt.scatter(iris.data[iris.target==1,0], iris.data[iris.target==1,1], color="blue")
plt.scatter(iris.data[iris.target==2,0], iris.data[iris.target==2,1], color="green")
plt.show()
knn_clf_all = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=50)
knn_clf_all.fit(iris.data[:,:2], iris.target)
KNeighborsClassifier(algorithm=’auto’, leaf_size=30, metric=’minkowski’, metric_params=None, n_jobs=1, n_neighbors=50, p=2, weights=’uniform’)
plot_decision_boundary(knn_clf_all, axis=[4, 8, 1.5, 4.5])
plt.scatter(iris.data[iris.target==0,0], iris.data[iris.target==0,1], color="red")
plt.scatter(iris.data[iris.target==1,0], iris.data[iris.target==1,1], color="blue")
plt.scatter(iris.data[iris.target==2,0], iris.data[iris.target==2,1], color="green")
plt.show()