Simple Linear Regression Implement
March 25, 2019
线性回归简单实现
根据上一小结得出的结论,简单实现一个线性回归算法。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.array([1,2,3,4,5], dtype=float)
y = np.array([1,3,2,3,5], dtype=float)
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.axis([0,6,0,6])
plt.show()
实现最小二乘法
\[a = \frac{\sum_{i=1}^m(x^{(i)} - \bar{x})(y^{(i)} - \bar{y})}{\sum_{i=1}^m(x^{(i)} - \bar{x})^2}\] \[b = \bar{y} - a\bar{x}\]x_mean = np.mean(x)
y_mean = np.mean(y)
num = 0.0
d = 0.0
a = np.sum((x - x_mean) * (y - y_mean)) / np.sum((x - x_mean) ** 2)
b = y_mean - a * x_mean
a
0.8
b
0.39999999999999947
y_hat = a * x + b
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.plot(x, y_hat, color='r')
plt.axis([0,6,0,6])
plt.show()
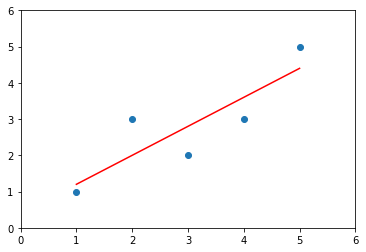
x_predict = 6.0
y_predict = a * x_predict + b
y_predict
5.2
使用自己封装的线性回归
import numpy as np
class SimpleLinearRegressionV1:
def __init__(self):
self.a_ = None
self.b_ = None
def fit(self, x_train, y_train):
assert x_train.ndim == 1 and y_train.ndim == 1,\
"needs single feature train data"
assert len(x_train) == len(y_train),\
"the size of x and y must be equals"
x_mean = np.mean(x_train)
y_mean = np.mean(y_train)
self.a_ = np.sum((x_train - x_mean) * (y_train - y_mean)) / np.sum((x_train - x_mean) ** 2)
self.b_ = y_mean - self.a_ * x_mean
return self
def predict(self, x_predict):
assert isinstance(x_predict, (int, float)) or x_predict.ndim == 1,\
"needs single feature data to predict"
assert self.a_ is not None and self.b_ is not None,\
"must be fit before oredict"
return self.a_ * x_predict + self.b_
def __repr__(self):
return "SimpleLinearRegressionV1()"
slr = SimpleLinearRegressionV1()
slr.fit(x, y)
SimpleLinearRegressionV1
slr.predict(x_predict)
5.2