kNN Intro
February 4, 2019
kNN 算法
邻近算法,或者说K最近邻(kNN,k-NearestNeighbor)分类算法是数据挖掘分类技术中最简单的方法之一。 所谓K最近邻,就是k个最近的邻居的意思,说的是每个样本都可以用它最接近的k个邻居来代表。
应用简单实现
根据下述过程可以看到,可以说kNN是一个不需要训练过程的算法。
k近邻算法是非常特殊的,可以被认为是没有模型的算法。
为了和其他算法统一,可以认为训练数据集就是模型本身。
- 首先我们自己造一个数据集
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
raw_data_X = [[3.393, 2.331],
[3.110, 1.782],
[1.343, 3.368],
[3.582, 4.679],
[2.280, 2.967],
[7.423, 4.697],
[5.745, 3.534],
[9.172, 2.511],
[7.792, 3.424],
[7.940, 0.792]]
raw_data_y = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
X_train = np.array(raw_data_X)
y_train = np.array(raw_data_y)
x = np.array([8.094, 3.366])
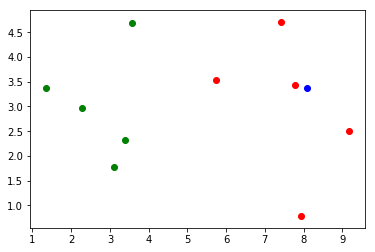
- 画散点图
plt.scatter(X_train[y_train==0,0], X_train[y_train==0,1], color='g')
plt.scatter(X_train[y_train==1,0], X_train[y_train==1,1], color='r')
plt.scatter(x[0], x[1], color='b')
plt.show()
- 我们封装一个我们自己的 kNN 算法
import numpy as np
from math import sqrt
from collections import Counter
def kNN_classify(k, X_train, y_train, x):
assert 1 <= k <= X_train.shape[0], "k must be vaild"
assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0], ("the size"
+ " of X_train must be equal to the size of y_train")
assert X_train.shape[1] == x.shape[0], ("the feature "
+ "number of x must be equal to X_train")
distances = [sqrt(np.sum((x_train - x) ** 2)) for x_train in X_train]
nearest = np.argsort(distances)
topK_y = [y_train[i] for i in nearest[:k]]
votes = Counter(topK_y)
return votes.most_common(1)[0][0]
- 使用我们自己封装的 kNN 算法
predict_y = kNN_classify(k=3, X_train=X_train, y_train=y_train, x=x)
predict_y
1
使用scikit-learn中的kNN
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
kNN_classifier = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=6)
kNN_classifier.fit(X_train, y_train)
KNeighborsClassifier(algorithm=’auto’, leaf_size=30, metric=’minkowski’,
metric_params=None, n_jobs=1, n_neighbors=6, p=2,
weights=’uniform’)
# 将要预测的数据放入一个矩阵
X_predict = x.reshape(1, -1)
y_predict = kNN_classifier.predict(X_predict)
y_predict[0]
1
重新整理kNN代码
我们模仿 sklearn 中的kNN实现,改造我们自己的 kNN 算法实现
- 面向对象
- 批量预测
import numpy as np
from math import sqrt
from collections import Counter
class kNNClassifier():
def __init__(self, k):
assert k >=1, "k must valid"
self.k = k
self._X_train = None
self._y_train = None
def fit(self, X_train, y_train):
assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0], ("the "
+ "size of X_train must be equal to the size of "
+ "y_train")
assert self.k <= X_train.shape[0], ("the size of "
+ "X_train must be at least k")
self._X_train = X_train
self._y_train = y_train
return self
def predict(self, X_predict):
assert (self._X_train is not None and
self._y_train is not None),("must fit "
+ "before predict")
assert X_predict.shape[1] == self._X_train.shape[1],\
("the feature number of X_predict must be equal"
+ " to X_train")
y_predict = [self._predict(x) for x in X_predict]
return np.array(y_predict)
def _predict(self, x):
distances = [sqrt(np.sum((x_train - x) ** 2)) for x_train in self._X_train]
nearest = np.argsort(distances)
topK_y = [self._y_train[i] for i in nearest[:self.k]]
votes = Counter(topK_y)
return votes.most_common(1)[0][0]
def __repr__(self):
return "kNN(k=%d)" % self.k
kNN_classifier_re = kNNClassifier(6)
kNN_classifier_re.fit(X_train, y_train)
kNN(k=6)
y_predict_re = kNN_classifier_re.predict(X_predict)
y_predict_re[0]
1